VPN connection service
Information Technology Team > VPN connection service
| 日本語 |
目次
1 Outline
1.1 Purpose of use
The VPN connection service provides secure access to your Department/laboratory subnet from external networks. Since it is not desirable for security reasons to directly disclose individual servers and printers to the outside, access to the internal network from the outside is basically denied at the School of Science. By using this service, users can access a file server or printer from a terminal connected to an external network in the same way as if they were directly connected to a network within a department or laboratory.
Access to journals contracted by university using this VPN service is not permitted. Please use the following university-wide services.
- EZproxy (for faculty, staff, and student): EZproxy
1.2 Service type
The School of Science offers a VPN service using client software and an L2TP VPN service using functions built into the OS. In VPN service using client software, department or laboratory managers need no special management of VPN service. L2TP VPN service is supported by many OS, so users can use it with relatively simple settings. See the table below for detailed differences.
| VPN service using client software | L2TP VPN service | |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation of department or laboratory manager | no | assing dedicated IP addresses for L2TP VPN service |
| host management | by MAC address for VPN interface (same as wired/Wi-Fi network) | no (no unique MAC address) |
| Environment | Windows (Difficult to use) Mac, Linux |
Windows, Mac, Android, iOS(iPad, iPhone) (Difficult to use) Linux |
| Authentication | Client Certificate | Password |
2 Supported users
- All faculty and students with the School of Science account.
- Users that can access to the department or laboratory network
- For L2TP VPN, department or laboratory manager need to assign IP adress in advance
3 Supported environment
- VPN service using client software
- Windows version has GUI
- Linux and Mac OS version is operated by command line (You need change the OS settings by yourself.)
- L2TP VPN service
- Windows, Mac OS X, Android, iOS (iPhone, iPad), etc
- Linux depends on distribution
4 Procedures for using the service
Access authentication is performed by using the same user certificate as for Wi-Fi authentication. The VPN connection service requires no other special procedures.
For the user certificate, see the page “Connection to Wi-Fi”. Note that the service does not accept a guest certificate for Wi-Fi (the guest certificate does not have Wi-Fi access to subnets within the School of Science).
5 Setup for L2TP VPN service
Please refer to the following page for the setting for each device.
For Windows 10, please refer to this setup guide.
5.1 Settings
- Server: vpn.adm.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
- Pre-shared key: Ask the network manager of your department or laboratory
- Account: School of Science account (10 digits)
- Password: Password of School of Science account
- Security: PAP
5.2 Other settings
You can set parameters manually for Linux etc.
- Phase1 Algorithms: aes256-sha1-modp1536
- Phase2 Algorithms: 3des-sha1-modp1536
6 Setup for VPN Service using client software
6.1 Downloading/installing client software
The VPN connection service is based on SoftEther VPN. Visit the link below to download the client software for service connection and then install it. Download the relevant latest version by clicking the corresponding link.
For Windows, navigate through the directories VPN -> Japanese -> Windows -> SoftEther VPN Client and select the platform type (“Intel x86, 32-bit” or “Intel x64 or AMD64, 64-bit” depending on the Windows version) to download the client software.
A manual with setup instructions is available at the link below.
6.2 Settings
- Host Name: vpn.adm.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
- Port Number: 443 (default)
- Virtual HUB Name: sos (Select from the list (no other options available).)
- Authentication Type: Client certificate authentication (Select from the list.)
- User Name: User’s 10-digit Universal ID
- Specify Client Certificate: Specify the user certificate downloaded from the School of Science authentication system.
6.3 Setup tips for Windows
Run the downloaded file to start the installer and complete the installation process as instructed. The user must indicate his/her agreement to the license terms. All settings may remain unchanged.
Upon initial installation, a virtual network adapter must be created. Start the SoftEther VPN Client Manager and choose [Virtual Adapter] -> [Create Virtual Network Adapter]. The virtual network adapter can be named arbitrarily. If a warning message regarding driver installation appears during the creation process, allow the installation of the driver (a message may also appear after the installation to confirm whether it has completed successfully).
The newly created virtual network adapter is assigned a MAC address different from that of the existing wired LAN or Wi-Fi network. If a MAC address registration is required for network access in the Department/Facility, inform the subnet administrator of the MAC address of the virtual network adapter.
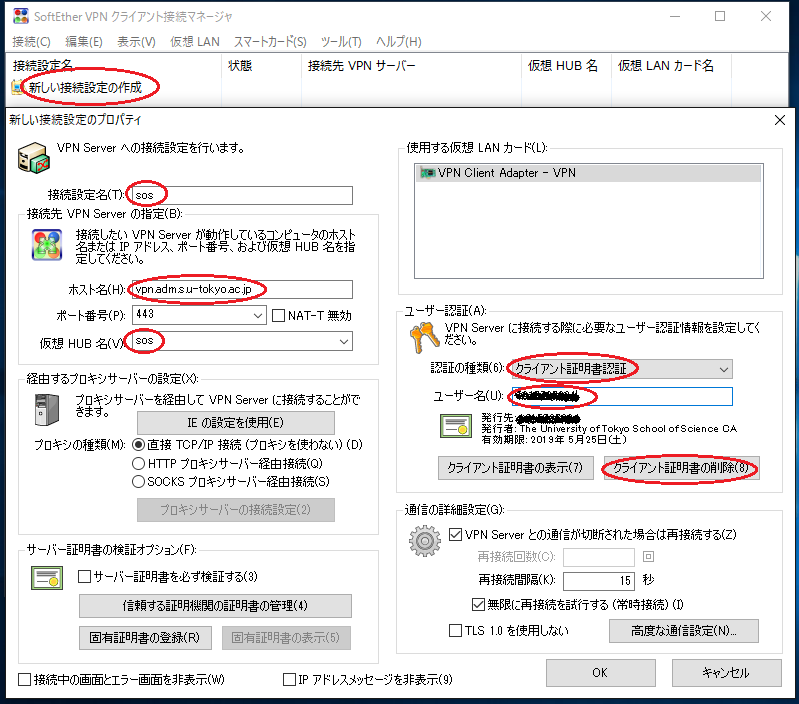
Then, configure the connection settings. Click [New VPN Connection Setting] to open the “New VPN Connection Setting Properties” dialog. The setting can be named arbitrarily. Fill in all required fields and click [OK] to create a new setting.
- The button to set the client certificate authentication is indicated as the [Close] button within a red circle below (since the screen below is the one after completing the setting, the button has been changed from [View Certificate] to [Close]).
After configuring the VPN connection setting, a connection can be made by double-clicking “Connect”.
6.4 Setup tips for Linux
The client software for Linux is a connection tool using the command line and does not have a GUI. It requires the user to load the certificate and to configure the network settings (the SoftEther manual warns that the Linux version of VPN Client is recommended for use only by users with a deep understanding of the Linux operating system and networks).
Client software installation requires utilities (such as make, gcc, and binutils) and development libraries (also known as “devel”) (such as libc (glibc), zlib, openssl, readline, and ncurses).
Unzip the downloaded file into the destination directory and execute the “make” utility to install the software. After running the vpnclient command, the software can be operated by the vpncmd command (selecting “2” upon startup enables the control by vpnclient).
Upon initial installation, a virtual network adapter must be created, as is the case with the Windows version. Use vpncmd to execute the following command (the virtual network adapter can be named arbitrarily).
NicCreate vpn
All necessary information must be extracted from the user certificate in advance. In the example below, XXXX.p12 represents the user certificate file name. The output file can be named arbitrarily.
openssl pkcs12 -in XXXX.p12 -nocerts -nodes -out XXXX.key openssl pkcs12 -in XXXX.p12 -clcerts -nokeys -out XXXX.crt
Execute the following commands to create a new VPN connection setting. In the example below, the setting name is sosvpn (the setting may be named arbitrarily). XXXX and NICNAME represent Universal ID and the name of the created virtual network adapter, respectively.
AccountCreate sosvpn /SERVER:vpn.adm.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp:443 /HUB:sos /USERNAME:XXXX /NICNAME:vpn AccountCertSet sosvpn /LOADCERT:XXXX.crt /LOADKEY:XXXX.key
Use the following command to make a connection.
AccountConnect
After the connection has been made, the interface created above (vpn_vpn) is connected via VPN. Set the address and routing configuration in the same way as eth0. To disconnect the connection, use the following command.
AccountDisconnect